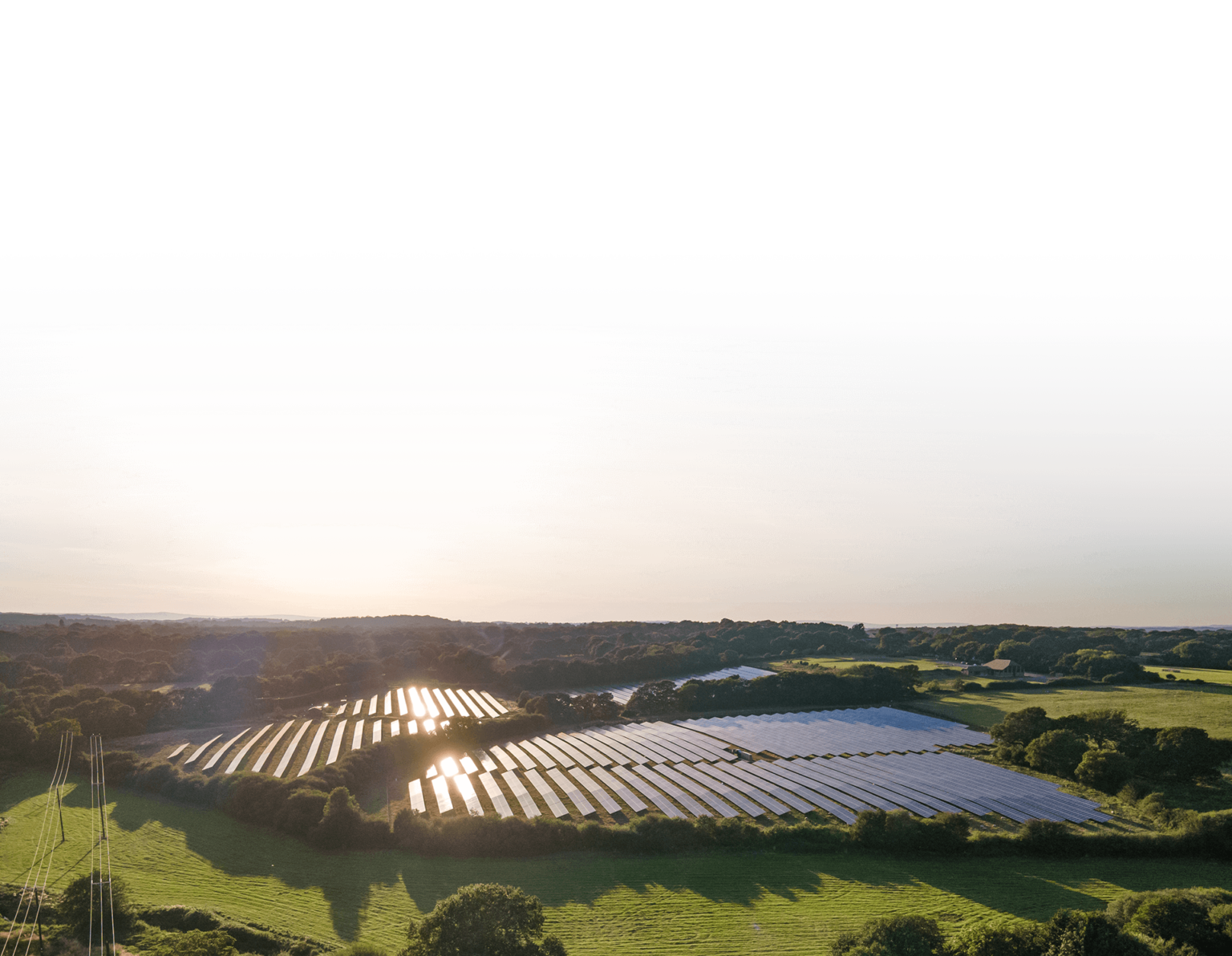
L’energia solare è ora la tecnologia di generazione elettrica a costo più basso.

Quello che è iniziato come un’iniziativa fortemente sovvenzionata per iniziare a ripulire il sistema elettrico basato sui combustibili fossili è diventato, grazie allo sviluppo rapido della tecnologia e della catena di approvvigionamento, un elemento chiave che funzionerà con energia elettrica pulita, a basso costo e prodotta localmente.
Il solare è la tecnologia di energia rinnovabile in più rapida crescita nel Regno Unito perché fornisce l’elettricità a più basso costo, è la più semplice da installare e può essere utilizzata per generare elettricità vicino ai villaggi, alle città e alle metropoli che ne hanno bisogno.
Nel 2022, la quantità di capacità di energia solare installata è stata il doppio rispetto all’anno precedente, e ciò è stato raggiunto senza alcun sussidio governativo. Tuttavia, a partire dal 2023, attualmente abbiamo solo il 20% della capacità di energia solare necessaria per raggiungere l’obiettivo del governo del Regno Unito di una rete elettrica a basso costo, priva di combustibili fossili e prodotta localmente entro il 2035.
Sostenere la transizione a lungo termine verso il trasporto e il riscaldamento a zero emissioni.
Nei prossimi 25 anni si prevede che la domanda di elettricità raddoppi, poiché le nostre auto a benzina e i sistemi di riscaldamento a gas verranno sostituiti da versioni elettriche per raggiungere l’obiettivo del Regno Unito di ridurre le emissioni di carbonio a zero entro il 2050.
Il basso costo, la semplicità e l’adattabilità dell’energia solare contribuiranno in modo significativo a soddisfare questa aumentata domanda di elettricità. Che si tratti di grandi impianti solari, dei tetti di case e aziende, o integrato nelle auto che guidiamo e nei dispositivi elettronici che utilizziamo.
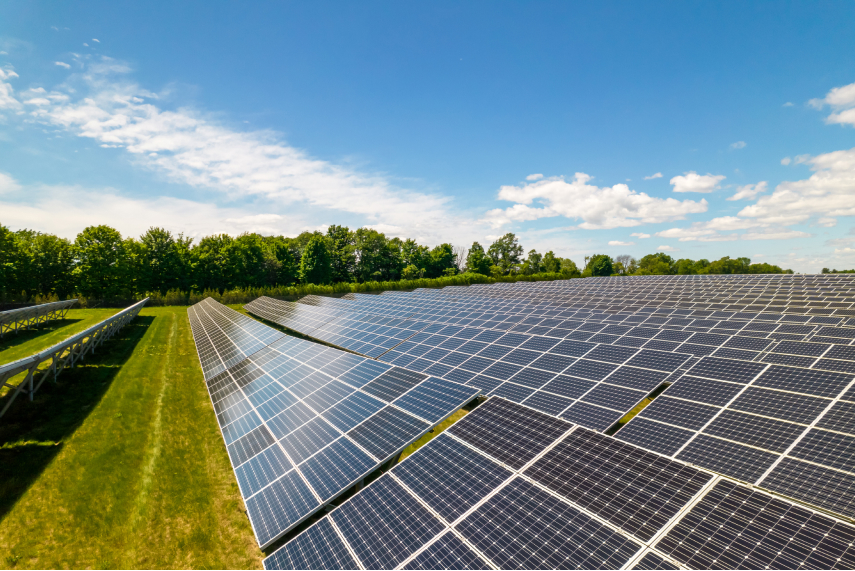

Che cos’è esattamente un impianto solare e come si costruisce?

I pannelli solari sono il componente fondamentale di un impianto solare. Contengono uno strato di silicio che trasforma la luce solare in corrente elettrica continua. Un inverter poi converte questa corrente in corrente alternata, che usiamo nelle nostre case e per trasportare l’elettricità attraverso il paese.
In un parco solare, i pannelli sono sollevati da terra su strutture metalliche e migliaia di pannelli sono collegati tra loro per generare abbastanza elettricità per alimentare una piccola città piuttosto che una singola abitazione. Il parco solare è collegato a una sottostazione elettrica vicina in modo che l’energia possa essere distribuita alle case e alle aziende locali.
I benefici dell’installazione di pannelli in un parco solare sono due. L’installazione è semplice e a basso costo, mentre si possono ottenere notevoli economie di scala installando migliaia di pannelli contemporaneamente. I pannelli possono anche essere posizionati senza le limitazioni delle forme dei tetti o dell’ombra degli edifici vicini, per garantire che catturino la massima energia solare disponibile. Insieme, questo permette ai parchi solari di generare elettricità al costo unitario più basso di qualsiasi tecnologia di energia rinnovabile.
Un tipico parco solare su larga scala produrrà abbastanza elettricità ogni anno per alimentare circa 15.000 case. La maggior parte dei parchi solari avrà anche uno stoccaggio delle batterie per consentire che parte dell’energia generata durante il giorno venga rilasciata nella rete durante la notte.
Anatomia di un progetto solare
Scopri i componenti principali di un impianto solare
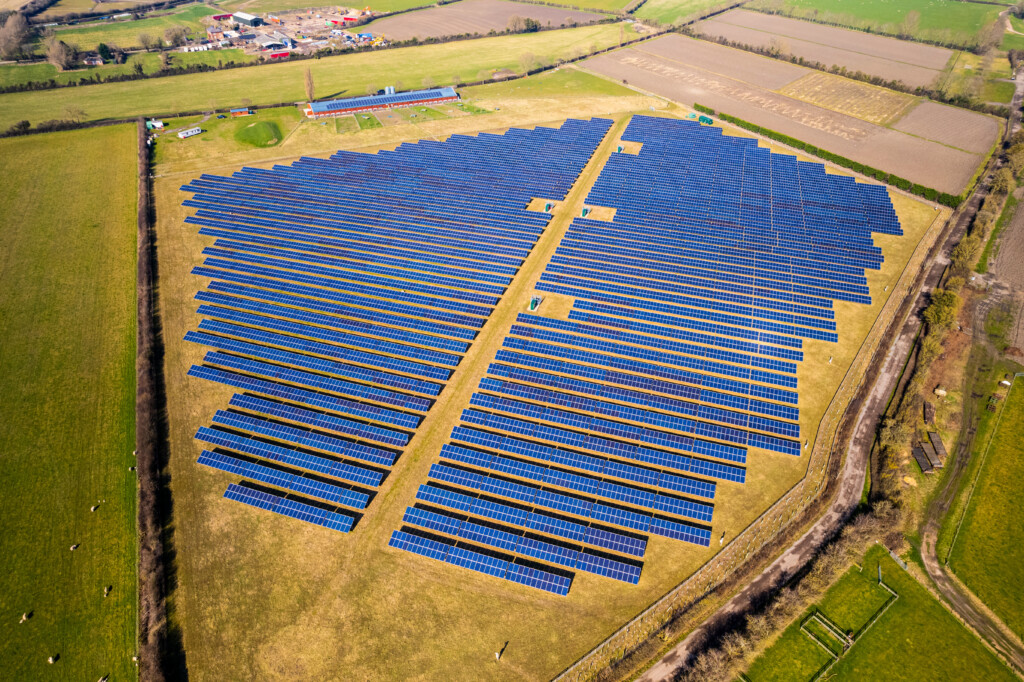

Contiene tutti gli elementi/interruttori necessari per connettersi alla rete elettrica locale.
Convertire la corrente da DC a AC
Aumenta la tensione per soddisfare la tensione richiesta dalla rete locale.
LAVORARE CON IL NOSTRO AMBIENTE
L’avanzamento continuo dell’agricoltura, delle abitazioni e dello sviluppo commerciale nel paesaggio naturale è anche un fattore che contribuisce al cambiamento climatico, riducendo la capacità degli ambienti naturali di immagazzinare carbonio e regolare i flussi d’acqua.
Abbiamo imparato dai primi progetti di parchi solari che un progetto ben progettato può aumentare significativamente la biodiversità e rafforzare gli ecosistemi naturali –
- La piantagione di fiori selvatici e erba intorno alle batterie e sotto i pannelli incoraggia gli insetti e i polinizzatori.
- L’uso di alberi e arbusti autoctoni per costruire i confini del sito crea nuovi habitat per la fauna.
- I sistemi di drenaggio naturale, utilizzando stagni, fossati e prati umidi, favoriscono insetti e anfibi.
- Ulteriori nuovi habitat vengono creati attraverso la costruzione di stagni, casette per pipistrelli e uccelli, collinette per farfalle e rifugi con mucchi di legna in tutto il sito.
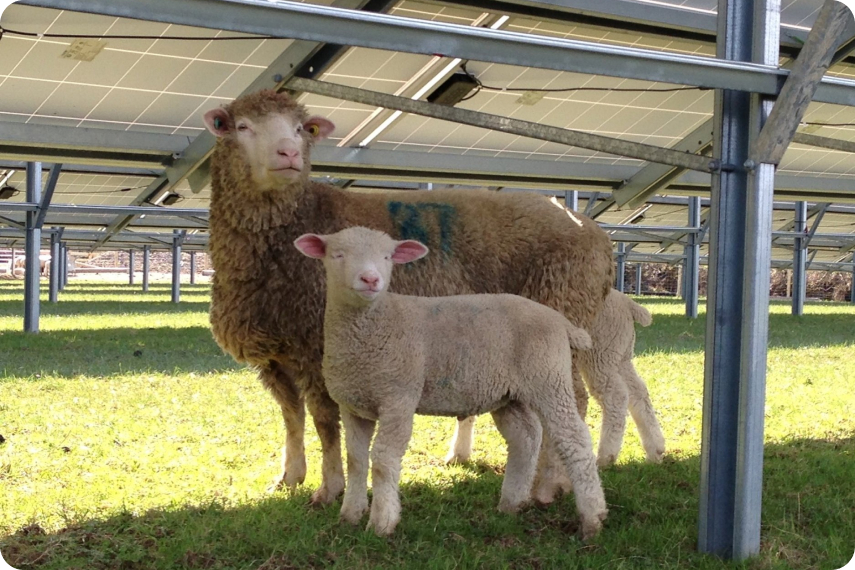

Ogni nostro progetto solare offre in media un aumento del 65% della biodiversità.
Progettato per garantire sicurezza, sostenibilità e minimizzare l’impatto sul quartiere.
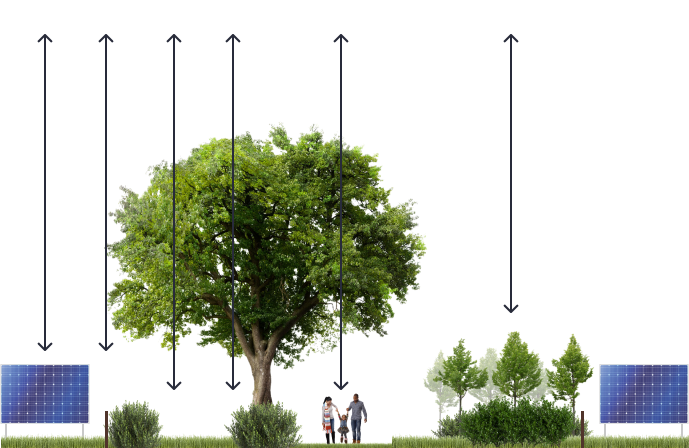
I siti dei progetti sono scelti con cura in base alla schermatura esistente da strade, sentieri, case e punti di vista elevati. Questo può includere alberi, siepi o caratteristiche naturali come pendii e creste. Ulteriori piantagioni aumentano la vegetazione ai confini, in modo che, dalla maggior parte dei punti di vista, anche da elevazioni naturali, il sito non sia visibile.
Mentre i pannelli solari e le batterie sono quasi silenziosi, le ventole di raffreddamento per gli inverter che convertono l’elettricità per la trasmissione alla rete elettrica locale e i contenitori di stoccaggio delle batterie producono un rumore a basso decibel quando sono in funzione. Queste unità sono solitamente posizionate lontano dai confini del sito, rendendo il rumore inaudibile per i residenti locali e i passanti.
Senza parti in movimento o liquidi, gli impianti solari sono considerati una tecnologia incredibilmente affidabile e sicura. Infatti, una volta operativi, la manutenzione si limita principalmente alla pulizia dei pannelli e alla falciatura dell’erba davanti ai pannelli, se il sito non è pascolato dalle pecore. Inoltre, senza fondazioni in cemento, un impianto solare è un’installazione leggera che può essere facilmente smontata e rimossa alla fine del ciclo di vita operativo del progetto, senza lasciare tracce durature sul terreno, ad eccezione della piantagione aggiuntiva e degli habitat naturali creati come parte del progetto. Esiste un mercato in crescita per il riciclaggio dei pannelli solari e si prevede che quasi tutti i materiali utilizzati nel progetto saranno riciclati dopo lo smantellamento.

Pannelli Solari
Recinzione per bestiame
Piantumazione di siepi
Piantumazione di siepi e alberi maturi
Sentiero pubblico
Piantumazione di arbusti e alberi